Ovarian Cysts: Types, Causes, Symptoms, Treatment
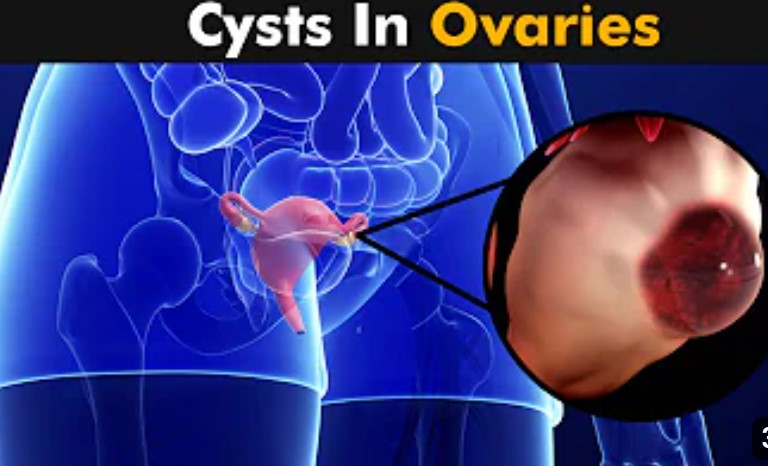
Ovarian cysts are sacs or pockets that are filled with fluid within the ovary or on its surface. Most women with ovarian cysts would commonly complain of pain!
What are Ovarian Cysts?
Ovarian Cysts are growth within the ovaries of a woman. The size of a cyst may vary from the size of an orange to the size of a very big watermelon. Recently, a 30-year-old woman, Kayla Rahn, of Alabama, in the United States, had surgery on the 26th of May, 2020 with the removal of an ovarian cyst weighing 50 pounds (22.6 kg). The woman had been experiencing stomach pains, and weight gain for a while before she went to the hospital and discovered that she had very large cysts. Even the medical team who performed the surgery confirmed that it was the largest cyst they had ever removed. The story according to Womens Health Mag.
If you do not understand what that weight means, 50 pounds is the weight of a half bag of foreign rice. That means this woman was carrying and walking around with half a bag of rice in her abdomen. I hope now, you can appreciate the weight of what the woman was carrying.
What is an ovary?
The ovaries are one of the organs that are responsible for reproduction and the formation of babies. It produces the eggs that form the child. They grow structures called follicles every month. These Follicles produce some hormones called estrogen and progesterone and release an egg during your ovulation.
Every woman has two ovaries, which are connected to the uterus (womb of the woman) with the help of a tube called the fallopian tube. The ovaries produce the eggs (which is the female gamete), and it meet the sperm (from the man) in the fallopian tube and fertilization occurs.
copyright 2018 Regents of the University of Colorado. All Rights Reserved. Created by Kristina DeRycke
What is the Cause of Ovarian Cysts
The ovarian cysts develop mostly due to your monthly menstrual cycle (these types of cysts are functional cysts and they are the most common). Other types of cysts are much less common.
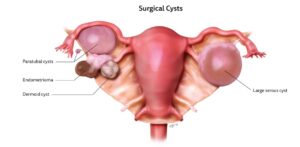
Types of Ovarian Cysts
There are different types of Ovarian Cysts as follows:
- Functional
- Inflammatory
- Germ cell Benign teratoma
- Sex cord-stromal
Functional ovarian cysts: Every month, the ovary releases an egg. If this fails, the follicle may keep growing and functional cysts are formed. Examples of this type of ovarian cysts are the follicular, corpus luteal, and theca luteal cysts.
- Follicular cysts: are formed when the follicle fails to rupture and release its egg but continues to grow in size.
The risk of developing functional cysts is reduced by the use of the combined oral contraceptive pill (COCP).
Inflammatory Ovarian Cysts: Inflammatory ovarian cysts are commonly seen in persons who have had a previous episode of pelvic inflammatory disease (PID) and are most common in young women.
The condition may involve the tube, ovary, and intestines. Read more about Pelvic Inflammatory diseases PID here.
Sometimes, the tube-ovarian mass can develop from other infective causes, for example, appendicitis.
Germ cell tumours: These are the most common type of ovarian tumors in young women between the ages of 20 and 40 years. The most common type of benign germ cell tumour is the mature dermoid cyst (cystic teratoma). In this type of tumour, things like hair, teeth, fat, skin, muscle, cartilage, or even bone may be seen in the ovaries. It has a low risk of becoming cancerous.
Sex cord-stromal tumours: These types of tumours are commonly seen in much older women. Some of them might have ovarian torsion as a result of the heaviness of the ovary.
Symptoms of Ovarian Cysts
Some persons with this condition may not notice any symptoms at all, whereas, others would have complaints of pelvic pain (lower back pain) which may start suddenly, or have been lasting for some time.
Some women may also notice the presence of a heavy mass or swelling in their abdomen. That is, they may notice their abdomen getting larger or heavier than normal.
In our environment, especially in the villages, with little to no access to medical care, some women might even think they are pregnant, but years would go by and they would not deliver and they would be wondering what is happening. Now is the time for you to try to reach that woman you know who has been pregnant for years, and people are asking her when she will deliver. She might just be carrying Ovarian cysts.
Treatment of Ovarian Cysts
Most women with ovarian cysts have little or no problems at all. Most times, the symptoms and cysts disappear without any treatment at all within a few months. However, anyone with these symptoms above should see a doctor as soon as possible to prevent the possibility of developing complications.
The treatment of ovarian cysts depends on the symptoms, size, and type of cyst.
Available options include;
Medications: In terms of inflammatory cysts like a tubo-ovarian abscess, antibiotics may be used.
Surgery: Ovarian cystectomy or even oophorectomy may be required through a laparoscopic approach.
Also, surgical drainage or excision may be employed in cases of an abscess.
Complications of Ovarian Cysts
The complications of ovarian cysts include;
- Haemorrhage: bleeding from cysts.
- Rupture: of the ovarian cysts.
- Torsion: twisting of the ovarian cysts around the stalk. It can also cause loss of blood supply to the ovaries.
Always see a doctor when you notice any changes in your body, especially if you have severe abdominal pain, pain with fever, or vomiting.
Do not delay, to avoid the risk of developing complications, which might end up causing you so much pain and loss of finances, without finding a permanent solution.
I hope you have been able to learn something new.
Feel free to ask any questions you may have below.