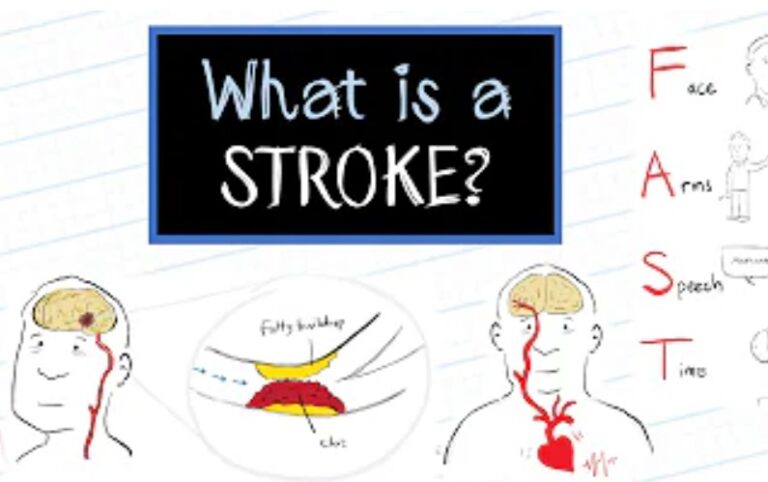
Ketamine Infusion Therapy: All You Need To Know
Ketamine infusion therapy has become a promising treatment option for various mental health conditions, including depression, anxiety, and post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD). This article will explore the benefits, risks, and considerations of ketamine infusion therapy as a treatment option.
Ketamine Infusion Therapy
Ketamine is a medication that has been used as an anaesthetic in medical procedures for many years. However, recent research has shown that ketamine may also have antidepressant effects when administered in lower doses. Ketamine infusion therapy involves administering a low dose of ketamine through an intravenous (IV) infusion for 40-60 minutes.

Benefits of Ketamine Infusion Therapy
Ketamine infusion therapy has several potential benefits as a treatment option for mental health conditions. One of the most notable benefits is the rapid onset of antidepressant effects. While traditional antidepressant medications can take several weeks to work, many patients report feeling the effects of ketamine infusion therapy within hours or days of the first treatment.
Ketamine infusion therapy may be effective for patients who have not responded to traditional antidepressant medications. This can be particularly beneficial for patients struggling with depression or other mental health conditions for an extended time.
Another benefit of ketamine infusion therapy is the potential for long-lasting effects. While patients may require ongoing treatments to maintain the benefits of ketamine infusion therapy, many patients report feeling the effects of the treatment for several weeks or even months following the last infusion.
Risks and Considerations
As with any medical treatment, there are some risks and considerations associated with ketamine infusion therapy. One potential risk is the potential for addiction or abuse of the medication. While the risk of addiction is relatively low when ketamine is administered in a clinical setting, patients with a history of substance abuse may not be appropriate candidates for ketamine infusion therapy.
Another consideration is the potential for side effects. While ketamine infusion therapy is generally well-tolerated, some patients may experience side effects such as dizziness, nausea, or hallucinations during or following the infusion. Patients should discuss concerns or questions with their healthcare provider before undergoing ketamine infusion therapy.
It is also important to note that ketamine infusion therapy may not be appropriate for all patients. Patients with a history of certain medical conditions, such as uncontrolled high blood pressure or heart disease, may not be candidates for ketamine infusion therapy. Additionally, pregnant or breastfeeding patients should not undergo ketamine infusion therapy.
Preparing for Ketamine Infusion Therapy
Patients considering ketamine infusion therapy should discuss the procedure with their healthcare provider to determine if it is an appropriate treatment option. Before the infusion, patients may be asked to stop taking certain medications, such as benzodiazepines or other sedatives, which can interfere with the effectiveness of the ketamine infusion.
Patients should also discuss concerns or questions with their healthcare provider before the infusion. This may include discussing the specific dose and duration of the infusion, what to expect during and after the procedure and any potential side effects or risks associated with the treatment.
After Ketamine Infusion Therapy
Following a ketamine infusion, patients may experience side effects such as dizziness, nausea, or blurred vision. These side effects typically subside within a few hours of the infusion, but patients should avoid driving or operating heavy machinery until the effects have completely worn off.
Patients should also monitor their symptoms following the infusion and report any concerns to their healthcare provider. Patients may sometimes require additional infusions or other treatments to manage their symptoms.
Alternatives to Ketamine Infusion Therapy
While ketamine infusion therapy can be an effective treatment option for some patients, it may not be appropriate or effective for all patients. There are
several alternatives to ketamine infusion therapy that patients may consider.
One alternative is electroconvulsive therapy (ECT), which involves passing an electric current through the brain to induce seizures. ECT is typically reserved for patients who have not responded to other treatments, as it can be a more invasive and intensive treatment option.
Another alternative is transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS), which uses magnetic fields to stimulate nerve cells in the brain. TMS is a non-invasive procedure that is typically administered in a series of sessions over several weeks.
Other alternative treatments may include psychotherapy, medication management, or alternative therapies such as meditation or yoga. Patients need to discuss these options with their healthcare provider to determine if they are appropriate and effective for their specific condition.
Ketamine infusion therapy can effectively manage mental health conditions such as depression, anxiety, and PTSD. By administering a low dose of ketamine through an IV infusion, the treatment can help to alleviate symptoms and improve overall function. However, some risks and considerations are associated with ketamine infusion therapy, which may not be appropriate or effective for all patients. Patients should discuss the benefits, risks, and alternatives with their healthcare provider to determine if ketamine infusion therapy is an appropriate treatment option for their condition.