Skincare for Cuts and Wounds Healing
Taking care of cuts and wounds is essential to maintaining good skincare hygiene. Proper wound care promotes faster healing, helps prevent infection, and minimizes scarring.
Here are some important guidelines for skincare for cuts and wounds:
- Cleanse the wound: Start by washing your hands thoroughly with soap and water before touching the wound. Gently clean the wound using mild soap and warm water. Avoid harsh antiseptics or hydrogen peroxide, as they can damage healthy tissue.
- Control bleeding: Apply gentle pressure to the wound using a clean cloth or sterile gauze to stop bleeding. Elevate the injured area if possible. For deeper or more severe wounds, seek medical attention immediately.
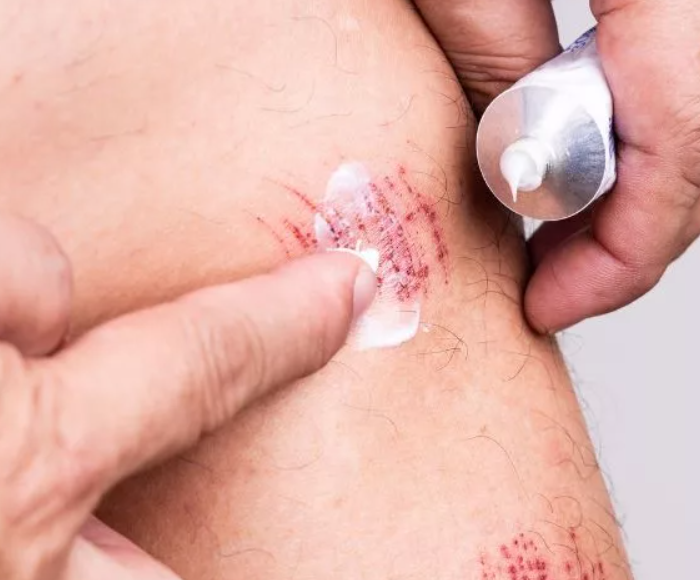
- Apply an antiseptic: Once the bleeding has stopped, you can apply a topical antiseptic to help prevent infection. Common antiseptics include povidone-iodine or chlorhexidine. Follow the instructions on the packaging for proper application.
- Protect the wound: Cover it with a sterile adhesive bandage or gauze pad to protect it from dirt, bacteria, and further injury. Change the dressing regularly or whenever it becomes wet or soiled.
- Keep the wound moist: Contrary to popular belief, keeping the wound moist can aid in the healing process. Use a sterile saline solution or an over-the-counter ointment to moisten the wound. This helps create an optimal environment for cell growth and prevents scab formation.
- Avoid picking at scabs: While scabs may form naturally, avoid picking or scratching them, as they can delay healing and increase the risk of scarring. Allow the scab to fall off naturally when the wound has healed underneath.
- Monitor for signs of infection: Watch for signs of infection, such as increased pain, redness, swelling, warmth, pus, or a foul odour. If you suspect an infection, seek medical attention promptly.
- Protect against sun exposure: Once the wound starts healing, it is important to protect the area from excessive sun exposure. Ultraviolet (UV) rays can cause hyperpigmentation and slow healing. Apply sunscreen with a high SPF and cover the wound with clothing or a bandage if possible.
- Eat a nutritious diet: A well-balanced diet rich in vitamins and minerals can support healing. Consume foods high in vitamins C, E, zinc, and protein to promote tissue repair and boost your immune system.
- Avoid smoking: Smoking can impair healing and increase the risk of complications. If you smoke, refrain from smoking until the wound has completely healed.
Also Read: Skincare for Bug Bites and Stings
Remember, if you have a deep or severe wound or are unsure how to care for a wound properly, it is always best to seek medical attention from a healthcare professional. They can provide specific guidance based on the severity and nature of the injury.