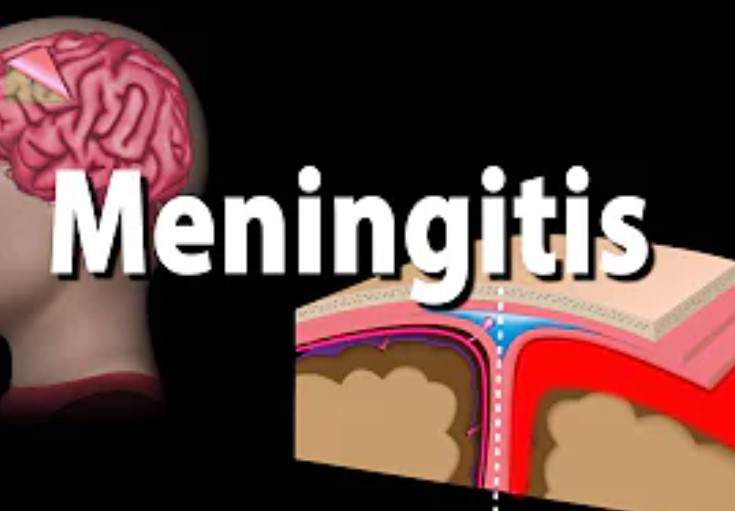
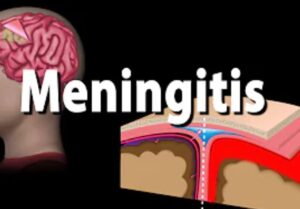
Meningitis: Causes, symptoms, prevention, Treatment!
Meningitis is a medical condition that arises as a result of inflammation of the protective covering of the brain (known as the meninges). The meninges protect the brain (just the way new products are wrapped in nylon to protect them). If it becomes infected, it swells (inflammation). This swelling of the covering is what is called meningitis.
This disease is much more common in children between the age of 1-5 (at the time when the brain is still growing), especially in the Northern Nigerian region (Meningitis Belt- 25 States + FCT).
Meningitis is both preventable & very treatable, but if left untreated, it can result in a lot of poor outcomes, including damage to the brain.
The organisms that cause meningitis can be prevented by proper vaccination of children following the NPI schedule. Mothers should always ensure to vaccinate their children to protect them from these vaccine-preventable diseases.
Causes of Meningitis
- Bacterial Meningitis: This swelling of the brain covering in our environment is mostly caused by bacteria, especially in children. The most common bacterial causes are organisms known as;
- Neisseria Meningitides,
- Haemophilus Influenza,
- Streptococcus pneumonia.
- Viral Meningitis: this is the most common cause for those in temperate countries (Europe, America, etc). It is less severe than the one caused by bacteria. Most times, it doesn’t require any treatment. It would resolve by itself.
- Tuberculous Meningitis: common in those with HIV & TB. Can be fatal if not treated.
Risk Factors for Meningitis (Things that can make you have it).
- Region: it is more common in persons living around the meningitis belt of Nigeria (25 states + FCT).
- Immunosuppression: This means poor immunity, which allows these organisms to thrive. This is commonly seen in malnourished children & those born to HIV-infected mothers who are not consistent with their medication.
- Anatomic defect: Children born with one or more defects (e.g.: a hole in the heart) are more prone to developing meningitis.
Symptoms of (How to know) Meningitis
The symptoms of the disease are common & can be mistaken with that of other common diseases like Malaria, hence an RDT for malaria must be done at the hospital to rule out malaria.
The symptoms include;
- Fever
- headache
- neck pain
- Neck stiffness
- Rashes
- back pain
- Convulsions/seizures: these are always happening and involve the whole body, not just a hand or a leg.
- Projectile vomiting, anorexia
- Locked Jaw: Older children with meningitis may walk around with a locked jaw for up to two days.
- Neck stiffness.
Diagnosis of Meningitis
To confirm that what is wrong with a person is meningitis, the person should be taken to the hospital where a procedure known as a Lumbar puncture would be done (at the person’s back), and some watery liquid known as CSF (cerebrospinal fluid) would be collected and then sent for test.
What do I do (treatment of Meningitis)
Meningitis is very treatable by medical personnel. Any person who is suspected of having meningitis should be taken to the hospital. The person would be properly taken care of, and given drugs including steroids & Antibiotics.
Please, do not attempt to treat at home, to prevent complications of poorly treated meningitis.
You can talk to us below to be referred to the best hospital nearest to your location.
Complications of Meningitis
Untreated or poorly treated meningitis, especially in a child, can lead to several poor outcomes such as;
- Deafness
- Blindness (cortical),
- Hydrocephalus: swelling/increase in the size of the head.
- Cerebral Palsy (CP): weakness of the limbs.
- Epilepsy: convulsions occurring frequently throughout life.
- Speech and language impairment
Prevention of meningitis
- Routine Immunization: Mothers should always ensure to take their children for Vaccination. Vaccines are safe & would protect your child from a lot of diseases that could kill them or leave them disabled (e.g. polio).
- Prophylactic drugs in the case of Neisseria Meningitides, given within 48 hours of diagnosis, for all patients in admission, household/schoolmates, and all health staff.
Remember: Meningitis is both preventable & Treatable. Let us spread the awareness today.