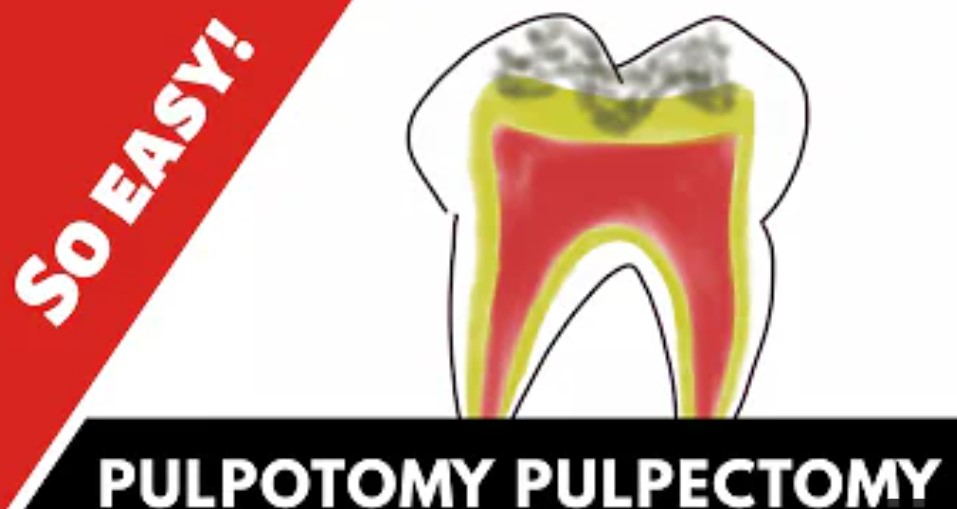
What is Pulpotomy: Advantage and Disadvantage
Dental problems are prevalent among children worldwide, and dental caries are among the most common oral health issues affecting them. Pulpotomy is a common dental procedure used to treat dental caries in primary teeth. This procedure involves the removal of the coronal pulp tissue, the infected or affected pulp tissue, leaving the root canal intact. A medicament is placed over the remaining root canal tissue, and the tooth is restored with a filling material. This article will explore the pulpotomy procedure, indications, techniques, and materials used in this dental treatment.
What is Pulpotomy
Pulpotomy is a common dental procedure performed on primary teeth with extensive caries or pulpitis. The procedure is recommended when there is a carious exposure of the pulp or when the pulp is inflamed due to trauma, caries, or other reasons. The decision to perform a pulpotomy is based on the clinical and radiographic examination of the tooth. The following are the indications for pulpotomy:
- Extensive caries involving the pulp: When caries affect the pulp, the pulp becomes inflamed and can cause pain, discomfort, and abscesses. A pulpotomy is performed to remove the infected pulp tissue and prevent the spread of infection to other teeth.
- Pulpitis: Pulpitis is the inflammation of the dental pulp. Trauma, caries, or other reasons can cause it. Pulpotomy is performed to treat pulpitis and prevent the infection from spreading.
- Trauma: Trauma to the teeth can result in pulp exposure, leading to inflammation and infection. A pulpotomy is performed to treat the inflamed pulp tissue and prevent the spread of infection.
- Pediatric endodontics: Pulpotomy is a common procedure in pediatric endodontics. It is performed to treat primary teeth and preserve them until permanent teeth emerge.
Pulpotomy can be performed using different techniques. The most common techniques are the traditional pulpotomy and the minimally invasive pulpotomy. The choice of technique depends on the extent of caries and the condition of the pulp tissue. The following are the two techniques used in pulpotomy:
Traditional Pulpotomy
A pulpotomy is a dental procedure involving removing the pulp tissue in the crown portion of a tooth while leaving the pulp tissue in the root canal intact. This procedure is typically performed on primary (baby) teeth with deep cavities or tooth pulp trauma.
In traditional pulpotomy, the dentist will first numb the area around the tooth with a local anesthetic. Then, the decayed or damaged portion of the tooth is removed, and a medicament, usually formoterol, is applied to the remaining pulp tissue in the tooth’s crown. The medicament is left for a few minutes to disinfect and preserve the remaining healthy pulp tissue.
After removing the medicament, a filling material, such as zinc oxide eugenol or glass ionomer, is placed over the remaining pulp tissue. The cavity is sealed with a temporary filling.
A traditional pulpotomy is a relatively quick and straightforward procedure to help save a damaged primary tooth from extraction. However, there are potential risks and side effects associated with using formoterol, including inflammation and allergic reactions, and alternative medicaments may be used instead.
Minimally Invasive Pulpotomy
Minimally invasive pulpotomy is a technique used in the treatment of primary teeth. This procedure involves the removal of the infected or affected coronal pulp tissue, leaving the healthy pulp tissue intact. The objective of a minimally invasive pulpotomy is to preserve the healthy pulp tissue and allow it to continue to function until the tooth is lost naturally. This procedure is a conservative approach to dental treatment and can help to minimize the need for future dental procedures.
The indications for minimally invasive pulpotomy are similar to those for traditional pulpotomy. It is recommended for primary teeth with extensive caries, pulpitis, or trauma. The decision to perform a minimally invasive pulpotomy is based on the clinical and radiographic examination of the tooth.
The technique for minimally invasive pulpotomy involves several steps. The following steps outline the procedure:
- Local Anesthetic: A local anaesthetic is administered to numb the tooth and surrounding tissues.
- Isolation: The tooth is isolated using a rubber dam to prevent saliva and other contaminants from entering the tooth during the procedure.
- Access Cavity: An access cavity is created in the tooth to access the pulp chamber.
- Removal of Infected Pulp Tissue: The infected or affected pulp tissue is removed from the coronal pulp chamber using a high-speed handpiece or a round bur.
- Hemostasis: A hemostatic agent such as ferric sulfate or aluminium chloride controls bleeding from the pulp chamber.
- Medicament Placement: A medicament such as mineral trioxide aggregate (MTA) or calcium hydroxide is placed over the remaining pulp tissue in the pulp chamber.
- Restoration: The tooth is then restored with a filling material such as glass ionomer cement or composite resin.
Minimally invasive pulpotomy has several advantages over traditional pulpotomy. These advantages include:
- Preservation of Healthy Pulp Tissue: Minimally invasive pulpotomy preserves the healthy pulp tissue, allowing the tooth to continue functioning until it is naturally lost.
- Reduced Post-Operative Pain: Since the healthy pulp tissue is preserved, there is less post-operative pain and discomfort.
- Conservative Approach: Minimally invasive pulpotomy is a conservative approach to dental treatment and can help to minimize the need for future dental procedures.
- Faster Healing: Healing time after minimally invasive pulpotomy is faster than traditional pulpotomy.
Minimally invasive pulpotomy has a few disadvantages as well. These include:
- Limited Long-Term Success: The long-term success of minimally invasive pulpotomy is limited, and the tooth may require further treatment.
- Technique Sensitive: Minimally invasive pulpotomy is a technique-sensitive procedure and requires experienced clinicians to perform the procedure.
The materials used in pulpotomy include:
- Local Anesthetic: Local anaesthesia is used to numb the tooth and surrounding tissues before the pulpotomy procedure.
- Disinfectant Solution: A disinfectant solution such as sodium hypochlorite or chlorhexidine is used to irrigate the root canal and disinfect the remaining pulp tissue.
- Hemostatic Agent: Hemostatic agents such as ferric sulphate or aluminium chloride control bleeding during the pulpotomy procedure.
- Pulpotomy Medicament: A pulpotomy medicament such as formoterol, mineral trioxide aggregate (MTA), or calcium hydroxide covers the remaining root canal tissue, aftHemostatic agents.
- Filling Material: A filling material such as nomer cement, composite resin, or amalgam is used to restore the tooth