Coronary Artery Disease: Causes, Prevention, Treatment
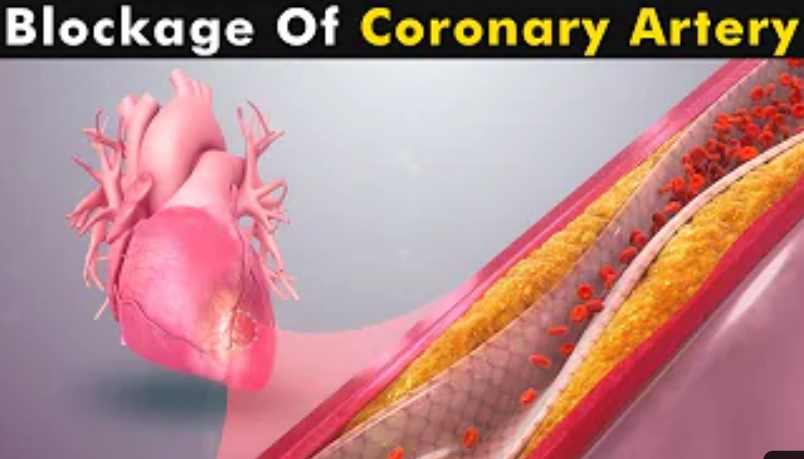
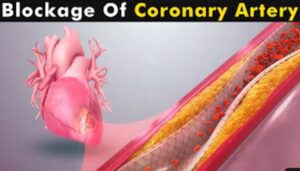
Coronary Artery Disease (CAD) occurs when there is a loss of blood supply to the muscles of a part of the heart or all of it. When the blockage affects of the heart, it can cause a heart attack.
Coronary artery disease (CAD) is the leading cause of premature death in Western nations and its rates are rising in Africa & Nigeria. In England, it has been estimated that about 1 in every 3 men and 1 in every 4 women die from CAD.
Heart attack also known as Myocardial Infarction is a form of CAD that happens when the total blood supply to the heart muscles is blocked. This results when a buildup of substances known as plaques usually due to fats/sugars narrow our blood vessels, thereby limiting blood flow to the heart. This can cause a heart attack.
When this happens, you may feel chest pain (known as angina pectoris), shortness of breath, or other coronary artery disease symptoms.
Cause of Coronary Artery Disease
The disease of the coronary arteries is almost always due to atherosclerosis and its complications, particularly
thrombosis.
What is Atherosclerosis
Atherosclerosis is a progressive inflammatory disorder of the arterial wall as a result of a deposit of atheroma (formed from lipids like cholesterol) which is not noticed until it grows in size and becomes big enough to block the coronary artery, leading to a loss of blood supply to the part supplied. When this happens, the muscles of the heart begin to die. This is what causes the pain and clutching of the chest that is usually seen in a person having a heart attack (CAD).
Symptoms of Coronary Artery Disease (CAD)/Heart Attack
CAD is characterized by central chest pain, discomfort, or breathlessness that is usually triggered by exertion or other forms of stress and is immediately relieved by rest. See the full symptoms of a heart attack here.
Risk Factors for Coronary Artery Disease (CAD)
The possible mechanism by which this heart attack occurs is very complex, but some known risk factors can cause a person to develop coronary artery disease. They include;
Age and sex: Age is the most powerful single risk factor that predisposes one to the development of atherosclerosis. It is common in the elderly population.
Family history: If any member of your family has had a heart attack in the past, there are possibilities that you can also have the disease. Hence, it is important to start efforts at prevention from an early stage.
This risk is further increased if the person is in the same environment (e.g. smoking, exercise, diet).
Hypertension: The incidence of atherosclerosis increases as Blood Pressure increases. Antihypertensive medications reduce the death that comes with the disease as well as prevent stroke.
Hypercholesterolaemia: Risk increases when you take a lot of cholesterol. It is very important to practice the habit of buying refined oil and other food products that are low in cholesterol. This helps to reduce the risk of cardiovascular complications (death, MI, stroke).
Diabetes mellitus: people with DM are also prone to developing heart disease. This is because, the excess sugar noticed in diabetes can be converted in the body to lipids, which can then lead to atherosclerosis, and hence, heart attack.
Lifestyle factors: There is a strong relationship between cigarette smoking and CAD. Alcohol is associated with reduced rates of coronary disease, but alcohol excess is associated with hypertension and cerebrovascular disease.
A sedentary lifestyle (Physical inactivity) and obesity are important risk factors for the development of atherosclerosis. Regular exercise helps to prevent this.
Diets deficient in fresh fruit & vegetables are associated with an increased risk of vascular disease. The importance of fruits and vegetables cannot be over-emphasized. read on the benefits of fruits and vegetables.
Management
Treatment principles for CAD are targeted at:
- Detecting and controlling risk factors.
- Control of Symptoms
- Detection of those who are at increased risk, for treatment to improve life expectancy.
Symptoms alone are a poor guide to the extent of coronary artery
disease. Stress testing can be used to identify potential persons who can have this condition.
What happens in stress testing is that the person is subjected to an amount of stress, through exercise for some minutes (3,6,9,12 minutes) in 4 different stages and the heart rate is observed during this time. This information is used to determine if he/she is at risk of developing the disease.
Identification and control of risk factors:
Before now, we have listed and explained some factors that place an individual at greater risk of developing the disease than others. The most important lifestyle modification that can be done is to quit cessation. However, there are other modifications such as;
- regular exercise
- aiming for ideal body weight.
- Statin therapy: Statin is a cholesterol-lowering drug that is used in the management of cholesterol. What the drug does is it block the enzymes in the liver that produce cholesterol, hence reducing the amount of endogenous cholesterol in the body, leaving you to deal with the exogenous ones (the ones you eat). All persons with CAD are advised to see their doctor and receive statin therapy, irrespective of their cholesterol concentration.
- Blood Pressure Management: Blood pressure should be managed properly and targeted to be kept at less than 140/85 mmHg at all times.
- Drugs: Some like Aspirin help in reducing the risk of adverse events from happening such as a Myocardial Infarction (MI) and should be prescribed indefinitely for all patients with CAD. You should see a doctor assess you and prescribe an appropriate dose that would be OK for you.
Clopidogrel is also an effective alternative in those persons that are intolerant of aspirin (e.g: patients with a risk of peptic (stomach) ulcer).
Relief of symptoms
Individuals with this condition are advised to avoid vigorous stressful activities, especially after a heavy meal or in cold weather.
When there is an attack, Sublingual glyceryl trinitrate (GTN) in spray or tablet form will usually help relieve the attack in about 2–3 mins. Persons with this condition can use GTN before engaging in any exercise that is likely to provoke symptoms. It is similar to the inhaler for those with Asthma.
Anti-anginal drugs: See your doctor for prescriptions.
How long can a Person live with CAD?
It has been observed that of the people who survive an acute attack, a good number of them, about 80% would live for an extra year. Around 75% can live for up to 5 yrs, while up to half of these people, (50%) can stay for 10 yrs. What determines how long a person lives with it is the amount of the person’s heart muscle that has been damaged as a result of the blockage of blood supply that happens in the disease.