Ovarian torsion: Symptoms, Causes, Treatment
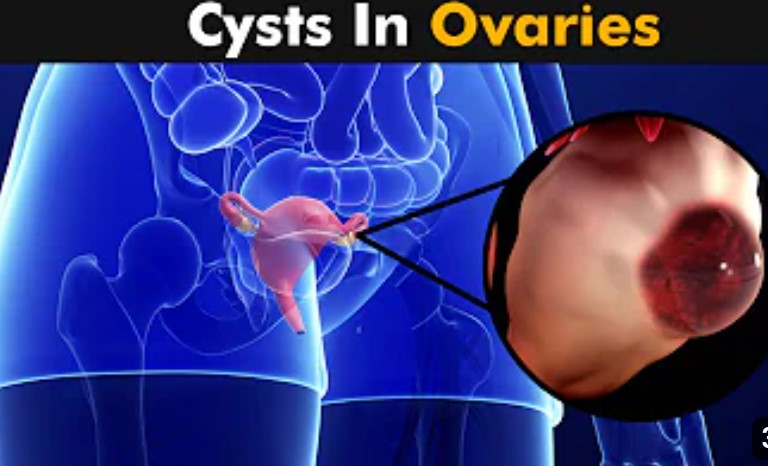
Ovarian torsion or Torsion of an ovary is a medical condition that occurs when the ovary or fallopian tubes twist on the tissues (the blood vessels that supply or drain blood from the ovaries or the ligaments that hold the ovary in place) that support them. This twisting compresses and cuts off the blood supply to the ovaries, and these symptoms cause severe pain in the pelvic area and can lead to death/damage to the ovaries.

Ovarian torsion commonly affects one ovary at a time but it does not mean that both ovaries cannot be affected at the same time.
Causes of Ovarian Torsion
The causes of Ovarian torsion could be due to;
- Enlargement of the ovary is seen in the presence of an ovarian cyst.
- it can also be caused as a result of a dermoid cyst.
Symptoms of Ovarian Torsion
Persons with ovarian torsion would show any of the following symptoms;
- lower abdominal pain that starts suddenly.
- nausea and vomiting.
- Abnormal Bleeding
You may experience cramps over several days or weeks. This happens when your ovary is twisting and untwisting constantly. Pain may also go into your back or legs. Depending on whether you’re post-menopausal or perimenopausal can affect the level of pain you feel.
In severe cases, if your ovary is necrotic and needs to be removed, you may have a fever. There will also be abnormal bleeding from your vagina, as well as discharge. If your abdomen or pelvic area is rigid or in pain when you stop touching your abdomen, you may already have a necrotic ovary. Your doctor may do a pelvic exam to feel for other problems and tenderness.
Torsion of the ovaries is one of the most common causes of acute pelvic pain.
Note: do not confuse these signs with those of ectopic pregnancies. Read ectopic pregnancy here.
Treatment of Ovarian Torsion
Anyone with this condition should see a doctor immediately. Some investigations, such as an abdominopelvic ultrasound scan might be requested to ensure that you indeed have the condition, and also verify the cause of the torsion.
The only treatment option for ovarian torsion is surgery. Emergency surgical treatment is required to untwist the ovary and restore blood flow, and any ovarian cyst, if noticed should then be removed. This would be done by a gynaecologist.
Your doctor will recommend one of the following two surgeries;
Laparoscopy. During this minor surgery, the doctor makes an incision in your abdomen and inserts a thin tube with a camera on the end, called a laparoscope. Then, they’ll untwist the ovary, and if needed, they’ll untwist your fallopian tube, too.
Laparotomy. This is an open surgery, which requires anaesthesia and possibly an overnight stay. Your doctor will make an incision in your abdomen and assess your reproductive organs. If possible, they’ll untwist and remove any present Cysts. This should be done without delay, to prevent complications that may arise. Source: WebMD
Complications of Ovarian Torsion
Any delay in the treatment of an ovarian torsion could lead to infarction and gangrene (that is death/rotting) may result, which would require the removal of the rotten ovary.
Can Ovarian Torsion Kill You?
For now, there has been no report of any person who died from torsion of the ovary. The worst complications that could arise from torsion of the ovary is the loss of the ovary or fallopian tube or both from rotting (necrosis), due to the loss of blood supply.
Does Ovarian Torsion Cause Infertility
When cases of torsion of the ovary are left untreated for a long time, it can lead to necrosis of the ovary as explained before, and this can in turn lead to problems with fertility. This is possible because they do not ovulate as frequently as when they had two ovaries. Regardless, most women still ovulate normally, conceive and have a normal pregnancy despite having a single functional ovary and fallopian tube.
You should seek immediate medical attention if you think your ovary is twisted, or you have any of the symptoms above. During surgery, your doctor will determine whether your reproductive organs will still be functional or not. They will then guide you through the right treatment plan.