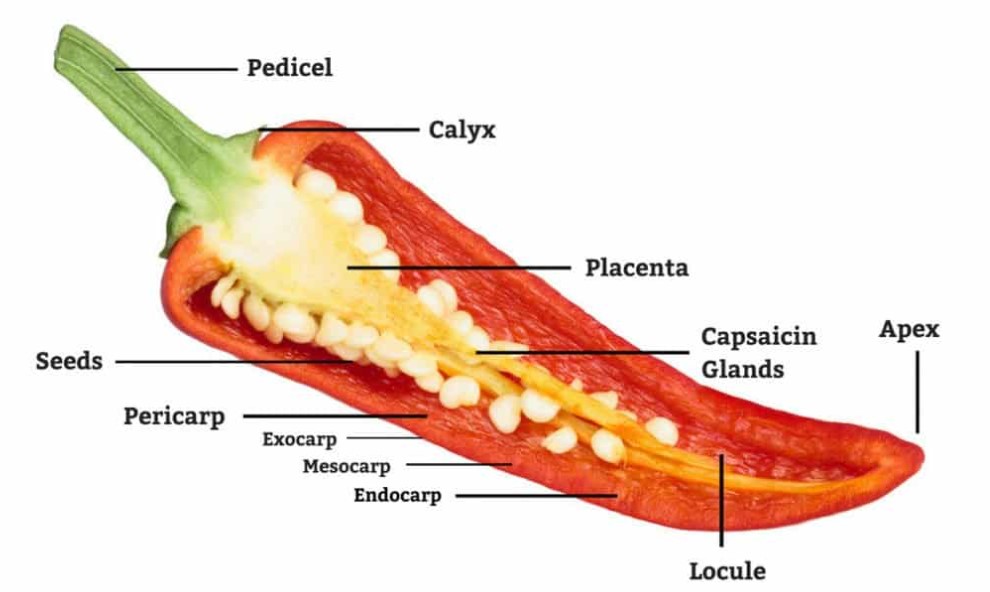
Longitudinal section of a fresh chilli pepper fruit
A longitudinal section of a fresh chilli pepper fruit reveals its internal structure and arrangement of various tissues.
Different parts in the Longitudinal section of a fresh chilli pepper fruit:
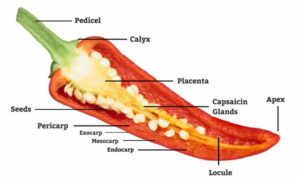
- Pericarp: The pericarp is the outermost layer of the fruit. A chili pepper is typically thin and smooth, consisting of several layers of cells. The pericarp protects the internal tissues and helps retain moisture.
- Placenta: Inside the pericarp, you would find the central core of the fruit, known as the placenta. The placenta extends from the stem end to the tip of the fruit. It is usually pale in colour and contains a high concentration of capsaicin, the compound responsible for the pepper’s spicy or hot taste.
- Seeds: The placenta houses numerous tiny, oval-shaped seeds embedded within a gel-like substance. The seeds are attached to the placenta through a stalk-like structure called the funiculus. Chilli pepper seeds are typically light tan to white and are spread by animals that consume the fruit.
- Mesocarp: Surrounding the placenta, you’ll find the fleshy mesocarp layer. The mesocarp is the bulk of the fruit and varies in thickness depending on the pepper variety. It is typically soft and juicy and contains most of the pepper’s flavour.
- Epidermis: The outermost layer of the mesocarp is known as the epidermis. It comprises a single layer of closely packed cells that help protect the underlying tissues.
- Vascular bundles: Running through the mesocarp, you’ll observe vascular bundles, which are structures composed of xylem and phloem tissues. These bundles transport water, nutrients, and sugars throughout the fruit.
- Pith: Towards the centre of the fruit, surrounding the placenta, you may find a spongy tissue called the pith. The pith provides structural support to the fruit and aids in nutrient storage.
Overall, a longitudinal section of a fresh chilli pepper fruit showcases the arrangement of the placenta, seeds, mesocarp, and pericarp. It highlights the distribution of capsaicin-rich tissues and gives insight into the anatomy of this popular spicy vegetable.
Also Read: Biology Specimen for WAEC 2023 and Answer